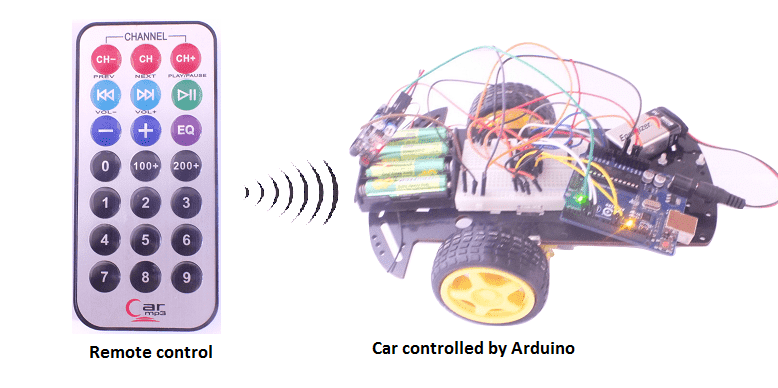

Presentation of robot car
A robot car is a type of robot that is designed to move on wheels or tracks, like a vehicle. It is typically controlled by a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or a Raspberry Pi, and can be programmed to move, sense its environment, and perform various tasks.
A robot car can be built using a variety of different components and technologies, depending on the specific application and design. The basic components of a robot car include a chassis, wheels or tracks, a microcontroller, and some type of power source such as batteries. Additional components may include sensors, such as ultrasonic sensors, infrared sensors, or cameras, to sense the environment, and actuators, such as motors, to control the movement of the robot.
There are different types of robot cars, some are controlled by a remote control, others have the ability to navigate autonomously using sensors and algorithms. Autonomous robot cars can be programmed to follow a pre-defined path, avoid obstacles, or even perform tasks such as mapping and exploration.
Building a robot car can be a fun and educational project, and it can be a good way to learn about robotics, electronics, and programming. However, it is important to note that building a robot car can be a challenging and time-consuming process that requires knowledge and experience in electronics, programming, and mechanics. Additionally, it’s important to ensure that the robot car is safe to operate, and it should be tested thoroughly before using it.
Presentation of a remote control car with Arduino
A remote control car with Arduino is a type of robot car that is controlled by an Arduino microcontroller and a remote control device. The Arduino receives signals from the remote control and uses them to control the movement of the car.
To build a remote control car with Arduino, you would need the following components:
- An Arduino microcontroller such as an Arduino Uno or Mega
- Motors and wheels to provide movement to the car
- A motor driver to control the motors
- A remote control receiver to receive signals from the remote control
- Batteries to power the car
- A chassis to hold all the components
- Wires to connect everything together
The Arduino would be programmed to receive the signals from the remote control receiver, and based on the received signals, it would control the movement of the motors by sending signals to the motor driver. The remote control can be any device that can send signals such as infrared or radio frequency.
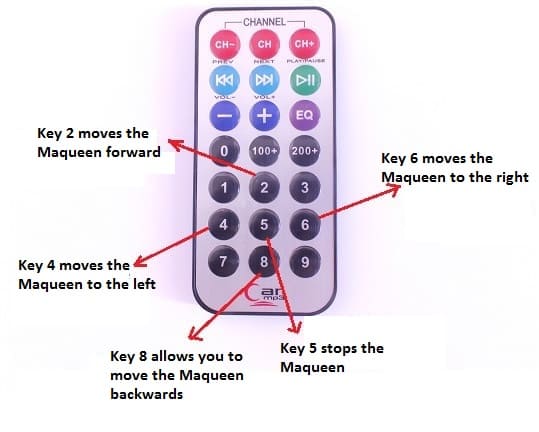
To control the car, the remote control will have buttons to move the car forward, backward, left and right. The Arduino program will be responsible for interpreting the signals sent by the remote control and translate them into actions on the car’s motors.
It’s worth noting that, building a remote control car with Arduino requires knowledge of electronics, programming and mechanics, as well as proper planning and design to ensure the car is safe to operate. Additionally, the system would require regular maintenance and updates to ensure it continues to function correctly.
Purpose of this project:
In this project we will build a remotely controlled car (by infrared) controllable by the Arduino board.
The user will be able to drive the car by a remote control in all four directions (forward, backward, right and left) and stop it.
Necessary components
Arduino UNO
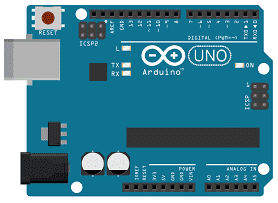
Arduino Uno is an open-source microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P microcontroller chip. It is one of the most popular and widely used boards in the Arduino family. It has 14 digital input/output pins, 6 analog input pins, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, a power jack, and an ICSP header.
The digital input/output pins can be used to connect sensors, LEDs, motors, and other components that can be controlled using digital signals. The analog input pins can be used to read the values of analog sensors, such as temperature sensors, light sensors, and potentiometers.
The USB connection is used to program the board and to communicate with a computer. The power jack can be used to power the board using an external power supply, while the ICSP header can be used for in-circuit programming and debugging.
The Arduino Uno board is compatible with a wide range of sensors, shields, and modules, making it a versatile and flexible platform for building various electronic projects. The board can be programmed using the Arduino IDE, a free software development environment that supports a simplified version of the C++ programming language.
The Arduino Uno is a popular choice for hobbyists, students, and professionals who want to experiment with electronics and develop their own projects.
SN754410 motor controller

The SN754410 is a quadruple half-H driver, also known as a motor driver or motor controller. It is a type of integrated circuit (IC) that can be used to control the speed and direction of DC motors and other inductive loads. The SN754410 is often used in robotics and other DIY electronics projects to control the movement of motors.
The SN754410 contains four half-H drivers, each of which can control the direction and speed of a DC motor. The IC can handle a maximum continuous current of 1A per channel, and a peak current of 2A per channel. It is compatible with a wide range of input voltages, from 4.5V to 36V, making it suitable for use with a variety of motor types.
The SN754410 is easy to use and can be controlled with a simple digital signal from a microcontroller or other control circuit. To use the SN754410, you simply connect the power supply, the motor(s), and the control signals to the appropriate pins on the IC. By toggling the control signals, you can control the speed and direction of the motor(s).
Remote control

A remote control is a device that allows for the remote operation of an electronic device or system. Remote controls can be used to control a wide range of devices such as televisions, air conditioners, cars, robots, and more. Remote controls typically use wireless technology such as infrared (IR) or radio frequency (RF) to send control signals to the device or system.
A remote control typically includes a set of buttons or a keypad that can be used to send control signals to the device or system. These buttons or keypad are usually labeled with the functions they control, such as power, volume, channel, or movement. Remote controls can also include additional features such as a display, a microphone, or an accelerometer.
A remote control is used to control the movement and actions of a robot car
IR sensor
The KY-032 is an infrared obstacle sensor module that is used to detect obstacles in front of a robot or other device. While it is primarily used for obstacle detection, it cannot be used for remote control directly. Remote control refers to the ability to control the movement and actions of a device or system wirelessly using a remote control or a smartphone.
In order to remotely control a robot car that uses the KY-032 obstacle sensor module, you would need to use a wireless communication module such as a radio frequency (RF) module or a Bluetooth module to establish a wireless connection between the robot car and the remote control device. The wireless control device, such as a remote control or a smartphone, would send control signals to the robot car via this wireless connection.
The robot car’s microcontroller, such as an Arduino, would be programmed to receive and interpret these control signals and then control the movement of the car’s motors and other actions based on the received control signals. The KY-032 obstacle sensor module would be used to detect obstacles in front of the robot car and send a signal to the microcontroller to take appropriate actions, such as stopping or avoiding the obstacle.
It’s worth noting that, while the KY-032 obstacle sensor module is not used directly for remote control, it can be used in conjunction with other components to create a remote controlled robot car. Additionally, it’s important to ensure the robot car is safe and reliable and the wireless communication is secure to prevent unauthorized access.
2 wheel car robot kit

A 2-wheel car robot kit is a collection of components that can be used to build a small, autonomous robot that moves on two wheels. These kits typically include a microcontroller, such as a ESP32 card, to control the robot’s movements, as well as motors, wheels, and other hardware to enable the robot to move and navigate.
2-wheel car robots are often used as educational tools, as they can be used to teach basic principles of robotics, electronics, and programming. They can also be used as a platform for experimenting with different control algorithms, sensors, and other hardware.
This robot kit is composed of:
-
car chassis.
-
2 gear motors (1:48)
-
2 car tires
-
1 universal wheel
connecting wires

Connecting wires are used to connect various components in an electronic circuit. They allow for the transfer of electricity, data, or signals between different devices and components.
When connecting wires to an Arduino or other microcontroller, it is important to pay attention to the correct pinout. The pinout refers to the arrangement of pins on the microcontroller and the corresponding function of each pin. The Arduino pinout can be found in the documentation provided by the manufacturer, or in various resources available online.
test plate

A test plate, also known as a test jig, is a device used to test electronic circuits and components. It is a board or plate that has been designed to hold and connect various components and devices in a specific configuration, allowing for the easy testing and measurement of their performance.
A test plate can be used to test various types of electronic circuits and components, such as microcontrollers, sensors, and actuators. It typically includes connectors and sockets for connecting wires, power supply and measurement devices such as multimeters, oscilloscopes, and power supplies.
construction of the car
Assembly of the car with Arduino
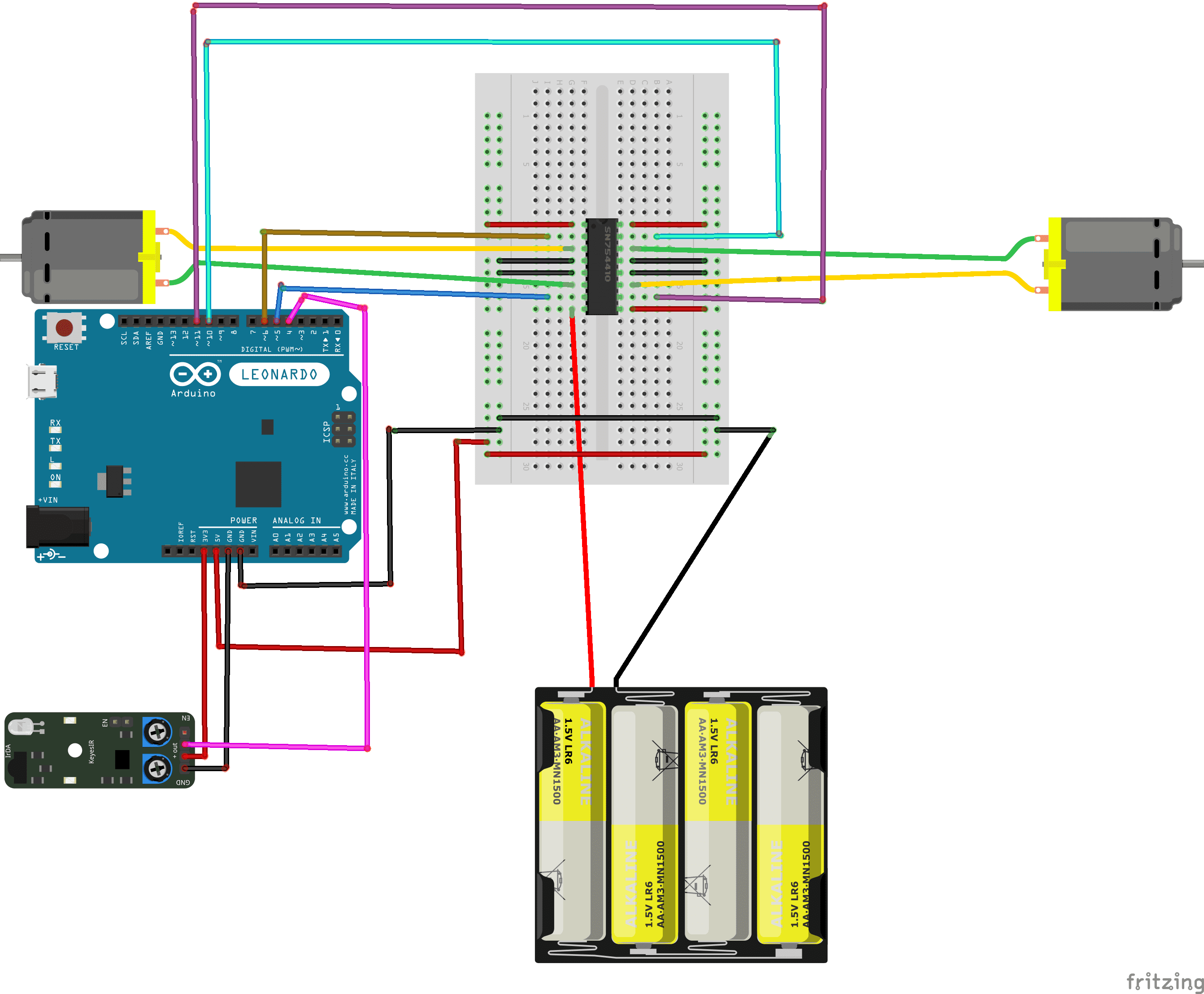
Program
Here is the program for the Arduino board connected to the car.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 |
#include <IRremote.h> int RECV_PIN = 4; IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN); decode_results results; int GA=11,GB=10,DA=5,DB=6; //pin initialization (GA & GB for left motor/ DA & DB for right motor) void setup() { irrecv.enableIRIn(); //Initializes the infrared receiver pinMode(DA,OUTPUT); pinMode(DB,OUTPUT); pinMode(GA,OUTPUT); pinMode(GB,OUTPUT); } /*******************************/ /***Function***/ void ar() //backward direction { digitalWrite(DA,HIGH); digitalWrite(DB,LOW); digitalWrite(GA,HIGH); digitalWrite(GB,LOW); } void av() //forward direction { digitalWrite(DA,LOW); digitalWrite(DB,HIGH); digitalWrite(GA,LOW); digitalWrite(GB,HIGH); } void d()//right direction { digitalWrite(DA,LOW); digitalWrite(DB,HIGH); digitalWrite(GA,HIGH); digitalWrite(GB,LOW); } void g()//left direction { digitalWrite(DA,HIGH); digitalWrite(DB,LOW); digitalWrite(GA,LOW); digitalWrite(GB,HIGH); } void s()//stop car { digitalWrite(DA,LOW); digitalWrite(DB,LOW); digitalWrite(GA,LOW); digitalWrite(GB,LOW); } /*****************************/ void loop() {if (irrecv.decode(&results)) { if (results.value==0xFF18E7)//press the 2 key av(); // the car is moving forward if (results.value==0xFF5AA5)//press the 6 key d(); // the car is moving right if (results.value==0xFF10EF)//press the 4 key g(); // the car is moving left if (results.value==0xFF4AB5)//press the 8 key ar(); // the car is moving backward if (results.value==0xFF38C7)//press the 5 key s();// car stops irrecv.resume(); //Get the following value } } |