Switching LEDs on and off with smartphone and Arduino

Arduino is an open-source electronics platform based on simple software and hardware. It can be used to control a wide variety of devices, including LEDs, motors, and sensors. Bluetooth is a wireless communication technology that allows devices to connect to each other over short distances. Arduino boards can be used with Bluetooth modules to enable wireless communication between devices. This can be used for a variety of applications, such as controlling a robot or sending sensor data wirelessly to a computer or phone.
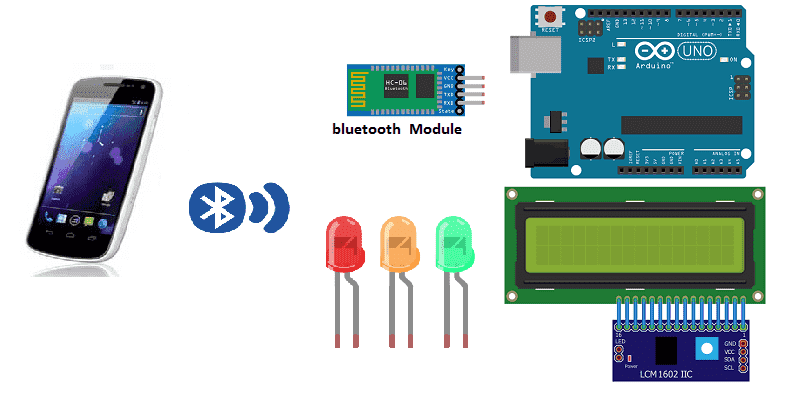
An Arduino board along with an HC-06 Bluetooth module and an LED can be used to create a simple project that allows for wireless control of the LED using a smartphone or other Bluetooth-enabled device. The Arduino board serves as the main controller, receiving commands from the Bluetooth module and controlling the LED accordingly.
The basic steps for this project would be:
- Connect the HC-06 Bluetooth module to the Arduino board.
- Connect the LED to the Arduino board, with the proper resistor in series.
- Write and upload a program to the Arduino board that controls the LED based on commands received from the Bluetooth module.
- Use a smartphone or other Bluetooth-enabled device to connect to the HC-06 Bluetooth module and send commands to control the LED.
This project is a good introduction to using Bluetooth with Arduino, and can be modified and expanded upon to create more complex projects.
Purpose of this tutorial:
In this tutorial, we will create a system allowing LEDs to be turned on and off (by Bluetooth) using the Arduino board and a smartphone.
We will create two programs: a mobile application with App Inventor for the smartphone and a program for the Arduino board.
Necessary components
Arduino UNO
The Arduino UNO is a popular model of the Arduino open-source electronics platform. It is based on the ATmega328 microcontroller and has 14 digital input/output pins, 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, and a power jack. The UNO also has a built-in USB-to-serial converter, which allows it to be programmed and communicate with a computer via a USB cable. The Arduino UNO can be used for a wide variety of projects, including controlling LEDs, motors, and sensors, as well as communicating with other devices via Bluetooth, WiFi, or other wireless technologies. It’s an easy-to-use board that can be programmed using the Arduino IDE, and is a good option for beginners and experts alike.
HC-06 Bluetooh module
The HC-06 Bluetooth module is a small, low-cost device that can be used to add Bluetooth functionality to a wide range of electronic devices. It is a slave-only device, meaning it can only connect to other Bluetooth devices, and cannot initiate connections itself. It is commonly used in DIY projects, such as adding wireless control to a robot or remote control to a device. It can be easily interfaced with microcontrollers such as Arduino and Raspberry Pi, and communicates via serial communication.
LCD I2C 160A Display
An LCD I2C 160A Display is a type of liquid crystal display (LCD) that uses the I2C communication protocol and is 160×128 pixels in resolution.
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) is a communication protocol that allows multiple devices to communicate with a single controller using only two wires. It is a more efficient method of communication compared to using multiple wires for data and control.
The display is controlled by an I2C controller that is built into the display, which communicates with an external microcontroller such as an Arduino board. The microcontroller sends commands and data to the display through the I2C interface, which controls what is displayed on the screen.
LEDs
An LED (light-emitting diode) is a type of semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current is passed through it. LEDs are commonly used in a wide range of applications, such as indicator lights, traffic signals, automotive lights, and electronic displays. They are also used in more advanced applications, such as in lighting systems, medical devices, and fiber-optic communications.
Test plate

A test plate is a type of device used in robotics to test the functionality and performance of various components or systems. It is typically a physical platform or structure that is designed to hold and support various test items or devices, such as sensors, actuators, motors, or other types of mechanical or electrical components. Test plates can be used to simulate different environments or conditions, such as temperature, humidity, vibration, or other factors, in order to evaluate the performance of the components or systems being tested. They can also be used to perform a variety of diagnostic or diagnostic tests, such as stress testing, endurance testing, or other types of evaluations.
Connecting wires

Wires are used to transmit electrical signals and power to various components such as motors, sensors, and microcontrollers. It’s important to properly route and secure the wires to prevent tangles and damage. There are several methods for doing this, including using cable ties, clamps, and wire looms. It’s also a good idea to use different colors or labeling to identify the different wires and their functions. When connecting wires in a robot, it’s important to follow proper safety procedures, such as using the correct wire stripper and connectors, and wearing protective equipment such as gloves and safety glasses.
Mounting
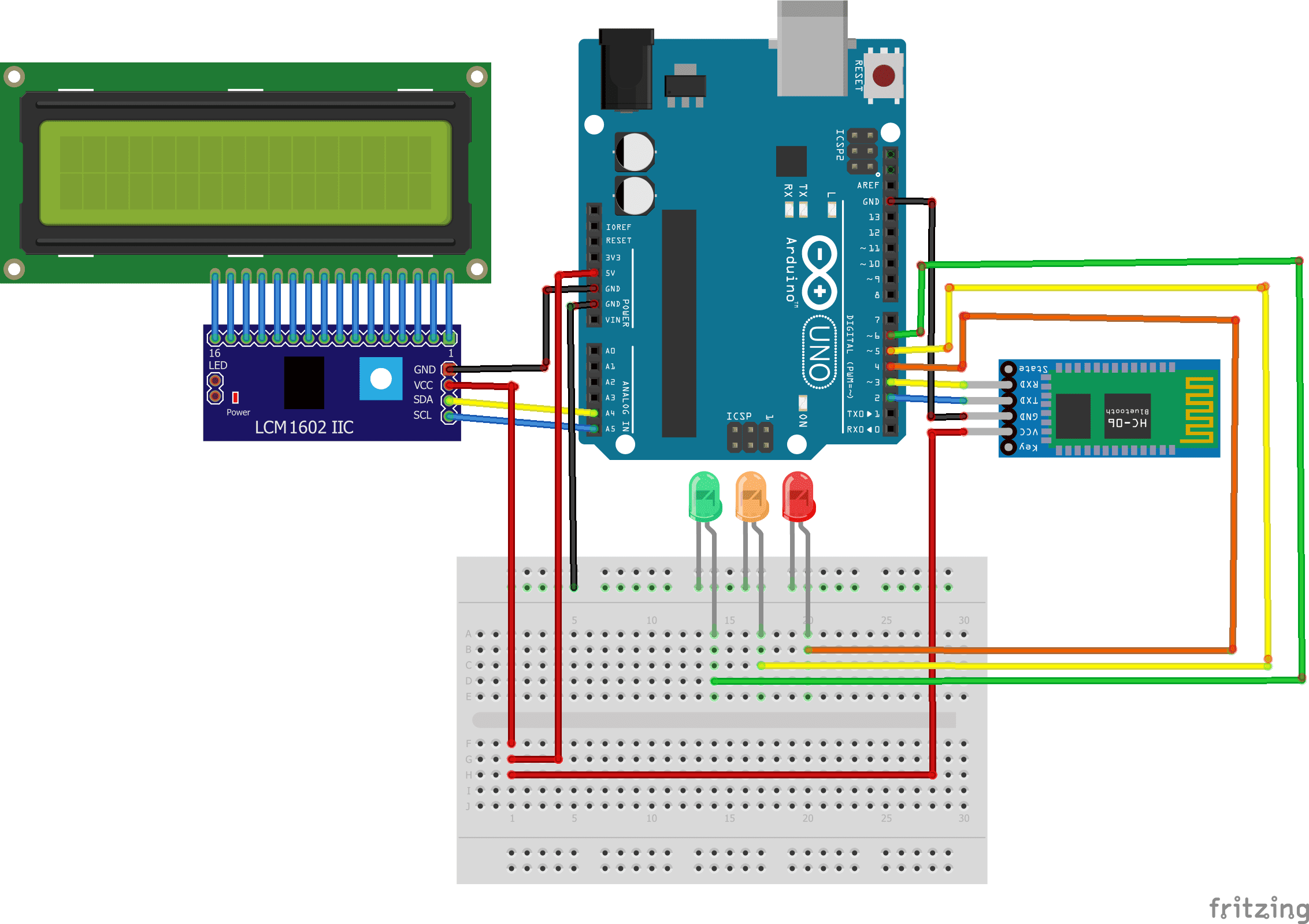
To carry out the assembly, you can connect:
-
the (-) terminals of the three GND LEDs of the Arduino.
-
red LED (+) terminal to digital pin 4 of Arduino
-
the terminal (+) of yellow LED to the digital pin 5 of the Arduino
-
the terminal (+) of green LED to the digital pin 6 of the Arduino
-
the GND terminal of the bluetooth module to GND of the Arduino
-
the VCC pin of the bluetooth module to the 5V pin of the Arduino
-
the RXD terminal of the bluetooth module to the digital pin 3 of the Arduino
-
the TXD terminal of the bluetooth module to the digital pin 2 of the Arduino
-
the SDA pin of the LCD display to A4 PIN of the Arduino
-
the SCL pin of the LCD display to A5 PIN of the Arduino
-
the GND pin of the LCD display to GND pin of the Arduino
-
the VCC pin of the LCD display to 5V pin of the Arduino
Program
Here is the program that allows you to connect the Arduino board to the smartphone and receive a message containing the order to turn the LEDs on or off.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
#include <SoftwareSerial.h> #include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h> LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 20, 4); SoftwareSerial hc06(2,3); String message=""; void setup(){ pinMode(btnPin,INPUT_PULLUP); pinMode(bouton, INPUT); lcd.init(); //Initialize Serial Monitor //Initialize Bluetooth Serial Port hc06.begin(9600); pinMode(4,OUTPUT); pinMode(5,OUTPUT); pinMode(6,OUTPUT); } void loop(){ lcd.backlight(); lcd.setCursor(0, 0); //Write data from HC06 to Serial Monitor if (hc06.available()){ message+=char(hc06.read()); lcd.clear(); lcd.print(message); }else{ if (message=="allumer_rouge") { digitalWrite(4,HIGH); // the red LED lights up } if (message=="eteindre_rouge") { digitalWrite(4,LOW); //the red LED goes out } if (message=="allumer_jaune") { digitalWrite(5,HIGH); //the yellow LED lights up } if (message=="eteindre_jaune") { digitalWrite(5,LOW); //the yellow LED goes out } if (message=="allumer_verte") { digitalWrite(6,HIGH); //the green LED lights up } if (message=="eteindre_verte") { digitalWrite(6,LOW); //the green LED goes out } message=""; } } |
Creation of the application with App Inventor:
We are going to create a mobile application named ‘allumer_leds_arduino’ with App Inventor which allows LEDs to be lit.
We propose to create the design of the application, with the following visual:
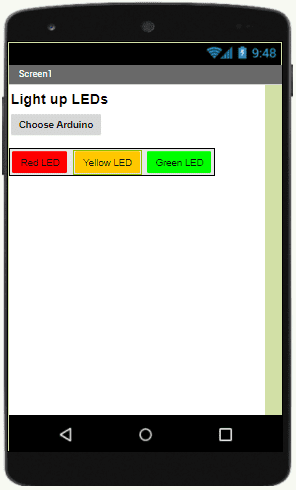
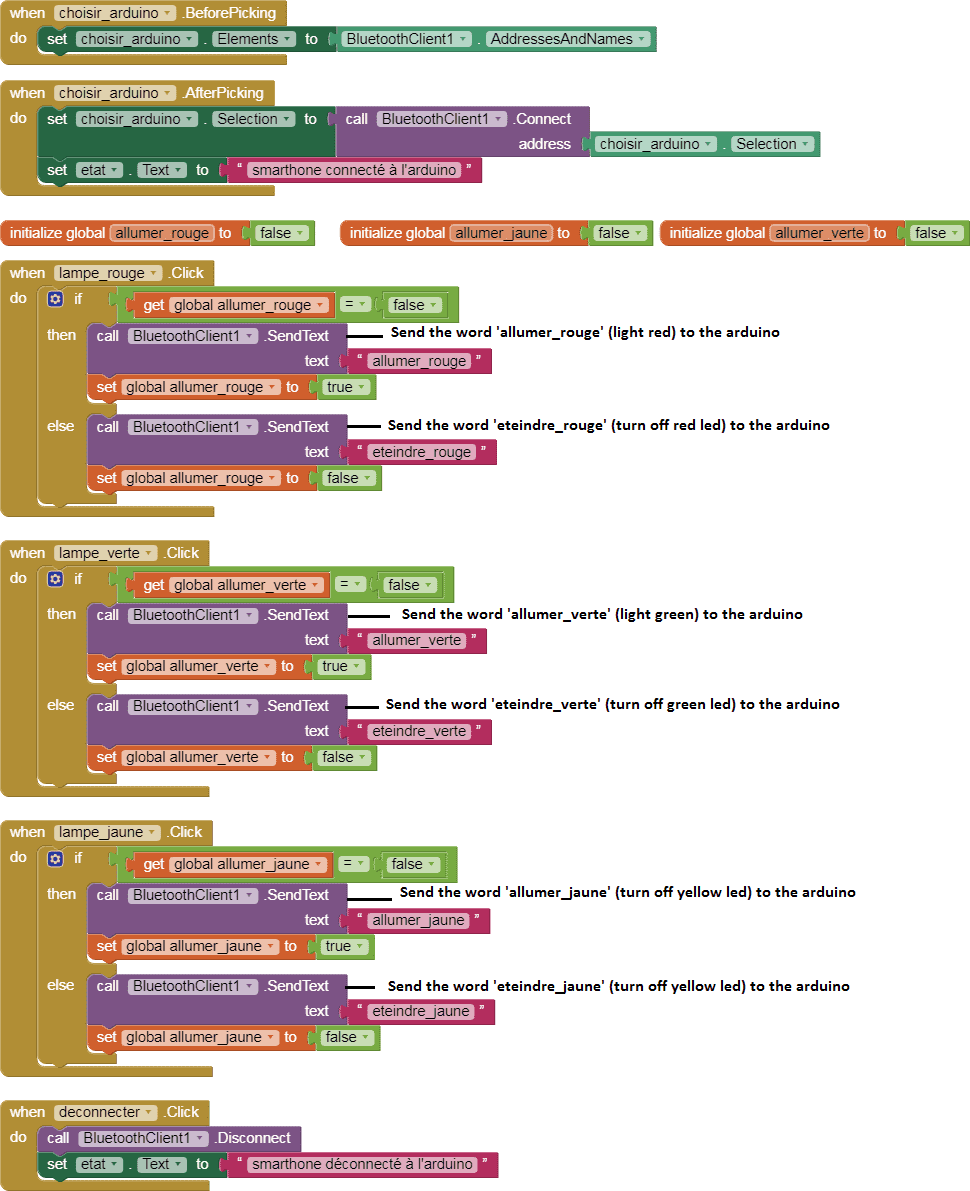
Programming with App Inventor
To program the application, App Inventor offers us to use the Blocks space, which allows you to create a program in the form of a block diagram. Very easy to use but requiring a little programming logic.
Here is the program of the application created in the Blocks area of the Inventor App: