Control LEDs by ESP32 and smartphone via Bluetooth

The ESP32 is a microcontroller that features Bluetooth connectivity. It can be used in a robot to provide wireless communication and control. To use the ESP32 in a robot, you will need to connect it to the robot’s hardware, such as motors, sensors, and other components. This can typically be done using wires. The ESP32 can then be programmed to control the robot’s movement and behavior using Bluetooth commands sent from a separate device, such as a smartphone or computer.
The ESP32 can be used to control an LED over Bluetooth. To do this, you will need to connect the LED to the ESP32 and write a program that sends Bluetooth commands to the ESP32 to turn the LED on or off.
Purpose of this tutorial:
A connected or intelligent LED corresponds to an LED that can be controlled remotely from a smartphone or tablet via the wifi or bluetooth network.
The connected LED is controlled by an electronic card programmed to communicate with Smartphone or tablet.
The objective of this tutorial is to remotely light 3 LEDs connected to the ESP32 board by a Smartphone via bluetooth.
That’s why we’re going to create two programs: a mobile application with App Inventor for the smartphone and a micropython program for the ESP32 board.
Necessary components
ESP32 card
An ESP32 card is a physical device that includes an ESP32 microcontroller and associated components, such as memory and input/output (I/O) pins. These cards are typically designed to be easily integrated into a project or prototype, and can be plugged into a breadboard or other prototyping platform.
ESP32 cards are often used in Internet of Things (IoT) projects, as the ESP32 microcontroller has built-in WiFi and Bluetooth capabilities, making it well suited for connecting to the internet and communicating with other devices wirelessly. These cards may also include additional features such as sensors, OLED displays, or other components that can be used in a project.
3 LEDs
An LED (light-emitting diode) is a type of electronic device that produces light when an electric current is passed through it. LEDs are widely used in a variety of applications because they are energy-efficient, long-lasting, and produce little heat. They are commonly used as indicator lights on electronic devices, as display backlights, and in lighting applications.
LEDs have a positive leg (anode) and a negative leg (cathode). The positive leg is typically longer and is connected to a power source, while the negative leg is connected to ground. When the LED is turned on, current flows from the positive leg through the LED to the negative leg, causing the LED to emit light.
test plate

A test plate is a type of device used in robotics to test the functionality and performance of various components or systems. It is typically a physical platform or structure that is designed to hold and support various test items or devices, such as sensors, actuators, motors, or other types of mechanical or electrical components. Test plates can be used to simulate different environments or conditions, such as temperature, humidity, vibration, or other factors, in order to evaluate the performance of the components or systems being tested. They can also be used to perform a variety of diagnostic or diagnostic tests, such as stress testing, endurance testing, or other types of evaluations.
connecting wires

Wires are used to transmit electrical signals and power to various components such as motors, sensors, and microcontrollers. It’s important to properly route and secure the wires to prevent tangles and damage. There are several methods for doing this, including using cable ties, clamps, and wire looms. It’s also a good idea to use different colors or labeling to identify the different wires and their functions. When connecting wires in a robot, it’s important to follow proper safety procedures, such as using the correct wire stripper and connectors, and wearing protective equipment such as gloves and safety glasses.
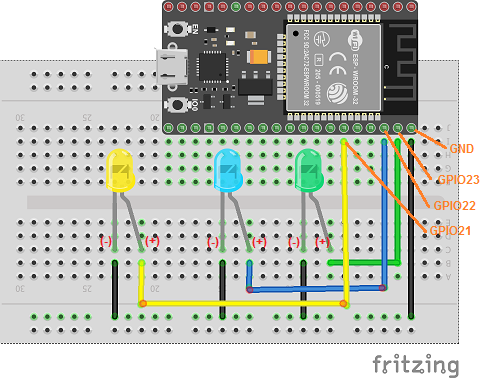
Assembly
To carry out the assembly it is necessary to connect:
-
the (-) terminals of the 3 LEDs to the GND pin of the ESP32 board
-
the green LED (+) pin to the GPIO23 pin of the ESP32 board
-
the blue LED (+) pin to the GPIO22 pin of the ESP32 board
-
the yellow LED (+) pin to the GPIO21 pin of the ESP32 board
Micropython program:
Here is the micropython program that allows you to connect the ESP32 card to the smartphone and remotely light 3 LEDs:
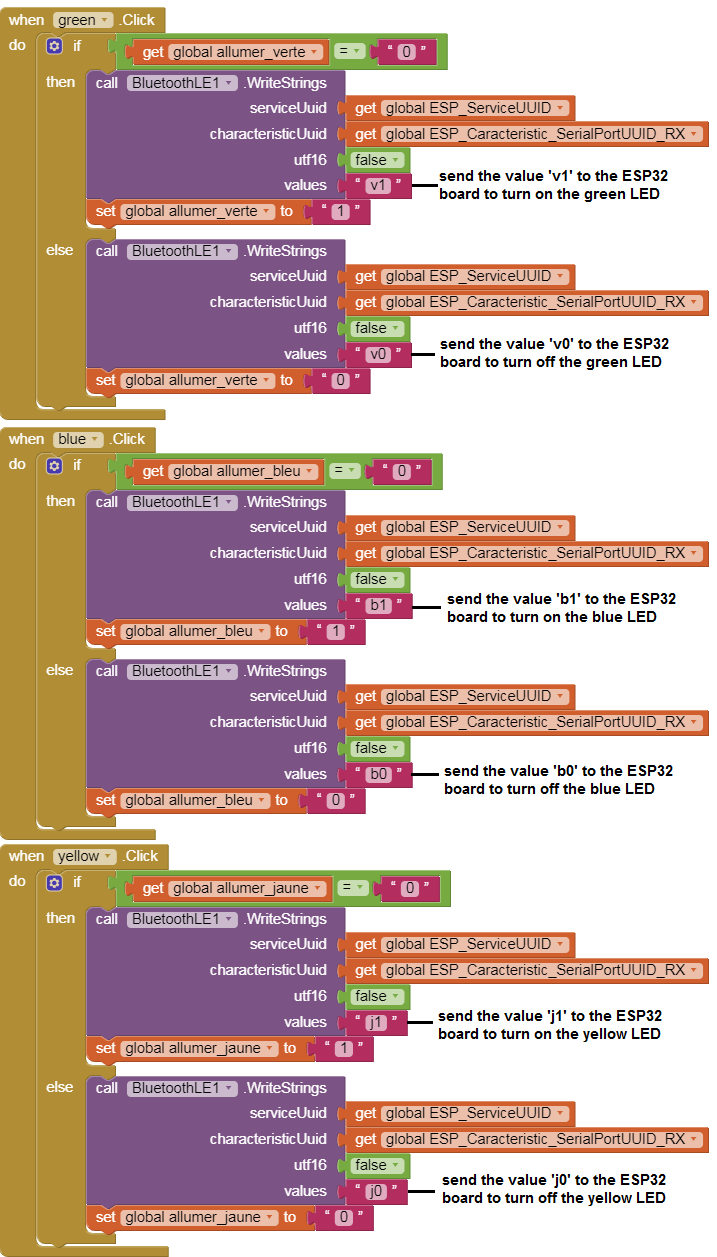
– If the ESP32 board receives the value ‘v1’ from the Smartphone, it lights up the green LED.
– If the ESP32 board receives the value ‘v0’ from the Smartphone, it turns off the green LED.
– If the ESP32 board receives the value ‘b1’ from the Smartphone, it lights up the blue LED.
– If the ESP32 board receives the value ‘b0’ from the Smartphone, it turns off the blue LED.
– If the ESP32 board receives the value ‘j1’ from the Smartphone, it lights up the yellow LED.
– If the ESP32 board receives the value ‘j0’ from the Smartphone, it turns off the yellow LED.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
########## IMPORT REQUIRED LIBRARIES ########## import bluetooth from ble_uart_peripheral import BLEUART from machine import Pin led_verte=Pin(23, Pin.OUT) led_bleu=Pin(22, Pin.OUT) led_jaune=Pin(21, Pin.OUT) # Create BLE object ble = bluetooth.BLE() # Open UART session for BLE uart = BLEUART(ble) # Define ISR for an UART input on BLE connection def on_rx(): # Read UART string, AppInventor sends raw bytes uart_in = uart.read() # lire le message recu du Smartphone via Bluetooth print("UART IN: ", uart_in.decode()) # display the message received from the Smartphone on the Thonny console if (uart_in.decode().find('v1')==0): led_verte.value(1) # turn on green led if (uart_in.decode().find('v0')==0): led_verte.value(0) # turn off green led if (uart_in.decode().find('b1')==0): led_bleu.value(1) # turn on blue led if (uart_in.decode().find('b0')==0): led_bleu.value(0) # turn off blue led if (uart_in.decode().find('j1')==0): led_jaune.value(1) # turn on yellow led if (uart_in.decode().find('j0')==0): led_jaune.value(0) # turn off yellow led # Map ISR to UART read interrupt uart.irq(handler=on_rx) uart.close() |
– You have to import these libraries :ble_uart_peripheral.py and ble_advertising.py.
– you must use the following firmware : esp32-20210902-v1.17.bin
Creating the application with AppInventor:
We will create a mobile application named ‘esp32_allumer_leds’ with App Inventor which allows you to connect the smartphone to the ESP32 board and remotely switch on 3 LEDs.
We therefore suggest that you create the design of the application, with the following visual:
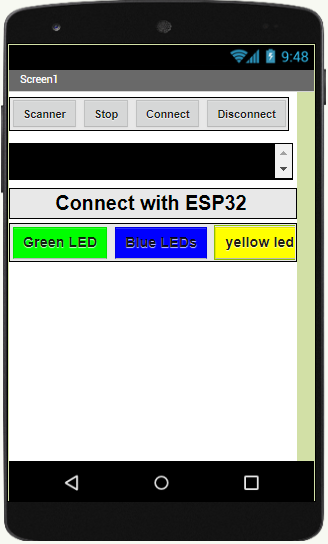
Programming with App Inventor
To program the application, App Inventor offers us to use the Blocks space which allows you to create a program in the form of a block diagram. Very easy to use but requires some programming logic.
Here is the program of the application made in the Blocks space of the App Inventor:
Remark:
After installing the mobile application on your Smartphone, you must follow these steps to connect to the ESP32 card you must:
-
Click on the ‘scan’ button
-
After finding the Micro:bit card, Click on the ‘Stop’ button
-
Press the name of the ESP32 board
-
Finally click on the ‘connect’ button
















mohamed ali 16-02-2323
bonsoir dans quel emplacement on sauvegarde les deux fichiers ble_uart_peripheral.py et "ble_advertising.py" sous thonny et merci "– You have to import these libraries :ble_uart_peripheral.py and ble_advertising.py."
Med Ali 17-02-2323
Salut il faut enregistrer ces deux fichiers dans la carte ESP32