
The HC-SR04 is an ultrasonic distance sensor that can be used to measure the distance to an object by sending out a sound wave and measuring the time it takes for the sound wave to bounce back. The ESP32 is a microcontroller with built-in WiFi and Bluetooth capabilities, which can be programmed using the Micropython. The SSD1306 is a monochrome OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) display that can be used to display text and graphics.
To use the HC-SR04 with an ESP32 and SSD1306 display, you will need to connect the HC-SR04 to the ESP32 according to the wiring diagram provided by the manufacturer. The HC-SR04 typically requires four connections: Vcc, Trig, Echo and GND.
Once the HC-SR04 is connected to the ESP32, you can use the ESP32‘s built-in pulseIn() function to measure the duration of the sound wave’s return trip. With this duration, you can calculate the distance to the object using the speed of sound.
To display the distance on the SSD1306 OLED display, you can use a library such as the SSD1306 library for Python. This library provides a set of functions for controlling the SSD1306 display, and it can be installed in the Arduino IDE and then included in your sketch.
You can use the library’s functions to initialize the display, clear the display, set the cursor position, and write text or graphics to the display.
Purpose of this tutorial:
In this tutorial we will learn how to use an HC-SR04 reference ultrasonic distance sensor with the ESP32 board.
Necessary components
ESP32
The ESP32 is a low-cost, low-power microcontroller with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities. It is a popular choice for IoT projects and is commonly used for a variety of applications such as home automation, wireless control, and sensor data logging. The ESP32 features a dual-core processor, a rich set of peripherals, and support for a wide range of protocols. It can be programmed using the Arduino IDE and various other programming languages such as C, C++, and MicroPython.
Additionally, the ESP32 has a wide range of features including:
- A high-performance processor with a clock speed of up to 240 MHz
- Support for various types of wireless connectivity such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
- Multiple communication interfaces such as I2C, SPI, UART, and I2S
- A large number of GPIO pins to connect to external devices and sensors
- A built-in security module for secure communication
The ESP32 is often used in projects where a low-cost, low-power device with Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities is needed, and it is commonly used with other sensors and devices to build IoT projects, home automation systems, wireless control systems, and data logging systems.
HC-SR04 sensor
The HC-SR04 is an ultrasonic distance sensor that can be used to measure the distance to an object by sending out a sound wave and measuring the time it takes for the sound wave to bounce back. It uses the principle of SONAR (Sound Navigation and Ranging) to detect the distance of an object.
The HC-SR04 sensor has four pins: Vcc, Trig, Echo, and GND. The Vcc pin is used to provide power to the sensor, typically 5V. The Trig pin is used to trigger the sensor to send out a sound wave. The Echo pin is used to receive the sound wave that bounces back from the object. The GND pin is used to ground the circuit.
When the Trig pin is set to a high voltage, the sensor sends out an 8-cycle sonic burst at a frequency of 40kHz. The sound wave travels through the air and bounces off any object in its path. When the sound wave hits an object, it bounces back and is received by the Echo pin. The sensor then measures the time it takes for the sound wave to travel from the sensor to the object and back, which is known as the « time of flight. » By using the speed of sound, we can calculate the distance to the object.
The HC-SR04 sensor has a range of 2cm to 400cm and can provide an accuracy of 3mm.
This sensor is widely used in a variety of applications such as robotics, security systems, and object detection systems. It’s a low-cost and easy-to-use sensor, making it a popular choice for hobby projects and DIY projects.
SSD1306 display
The SSD1306 is a monochrome OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) display that can be used to display text and graphics. It is a small, low-power display that can be easily integrated into a wide variety of projects.
The SSD1306 display is controlled using an I2C or SPI interface, which allows it to communicate with a microcontroller or microprocessor. It typically requires only a few connections to the microcontroller, such as Vcc, GND, SDA and SCL for I2C or SCK, MOSI, CS, DC and RST for SPI.
The SSD1306 display has a resolution of 128×64 pixels, and it can display text and graphics using a monochrome pixel format. The display has an integrated charge pump that allows it to operate at a voltage as low as 2.7V. This allows for low power consumption and makes it suitable for battery-powered projects.
The SSD1306 display can be controlled using a variety of libraries that are available for different platforms such as Arduino, Raspberry Pi, ESP32, etc. These libraries provide a set of functions for controlling the display and make it easy to use the SSD1306 display in your projects.
The libraries typically provide functions for initializing the display, clearing the display, setting the cursor position, and writing text or graphics to the display. They also provide functions for controlling the display’s contrast and brightness.
Overall, the SSD1306 display is a versatile and low-power display that can be easily integrated into a wide variety of projects. It is a popular choice for creating small, portable, and battery-powered devices such as digital clocks, temperature displays, and other small graphic displays.
Connecting wires

Connecting wires refers to the process of physically connecting wires or cables to a device or circuit in order to establish an electrical connection. This can be done by using various connectors such as plugs, sockets, or terminal blocks. The wires are typically color-coded to indicate their function, such as red for power, black for ground, and yellow for signals.
Test plate

A test plate is a type of circuit board that is used to test electronic components. It typically consists of a flat board made of a non-conductive material, such as plastic or fiberglass, with a number of holes or pads that are used to connect electronic components. The test plate allows you to connect electronic components and test them easily.
Mounting
The assembly is disconcertingly simple:
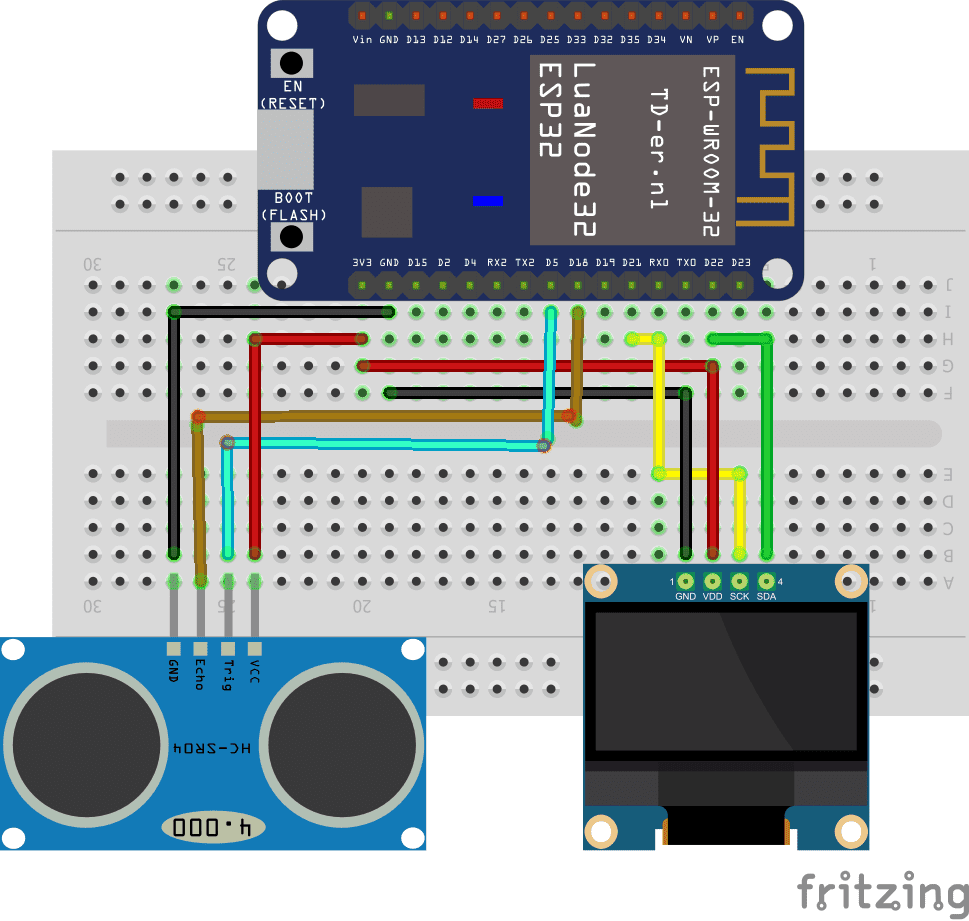
For HC-SR04 sensor :
-
The 3.3V power supply from the ESP32 board goes to the VCC pin of the sensor.
-
The GND pin of the ESP32 board goes to the GND pin of the sensor.
-
Pin D5 of the ESP32 board goes to the TRIGGER pin of the sensor.
-
Pin D18 of the ESP32 board goes to the ECHO pin of the sensor.
For SSD1306 display:
-
the SCL pin to pin D22 of the ESP32 board
-
the VCC pin to the 3.3V pin of the ESP32 board
-
the GND pin to the GND pin of the ESP32 board
-
the SDA pin the D21 pin of the ESP32 card
Micropython program
Here is the program that displays the distance in cm that separates the ultrasonic sensor from an obstacle.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
from hcsr04 import HCSR04 from machine import Pin,I2C import ssd1306,time i2c = I2C(scl=Pin(22), sda=Pin(21)) #Init i2c oled=ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(128,64,i2c,0x3c) sensor = HCSR04(trigger_pin=5,echo_pin=18,echo_timeout_us=1000000) while True: distance = sensor.distance_cm() print(distance,' cm') time.sleep_ms(100) oled.fill(0) oled.text("Distance:",30,20) oled.text(str(distance),30,40) oled.text("cm",30,50) oled.show() #display the distance between the sensor and a detected obstacle |
Note: the following two libraries must be imported: hcsr04 and ssd1306