Display a character on the MAX7219 display with Arduino

The Arduino UNO is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P. It has 14 digital input/output pins, 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button.
The MAX7219 is a serial input/output common-cathode display driver that can be used to drive a 7-segment LED display, or an 8×8 LED matrix. It can be controlled via a 3-wire serial interface, with the Arduino UNO, and requires only one digital output pin to control all 8 digits. With the help of the MAX7219 library, it is easy to control the MAX7219 display.
Purpose of this tutorial:
In this tutorial we will see how to display a character on the MAX7219 display with Arduino card.
Necessary components
Arduino UNO
The Arduino UNO is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P. It is a popular choice for beginners and hobbyists as it is easy to use and has a wide range of available libraries and tutorials. The board has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button. It can be programmed using the Arduino IDE, which supports C and C++ programming languages and has a simple and user-friendly interface. The board can be powered via USB or an external power source, and can be used to control and interface with various electronic devices and sensors.
MAX7219 display
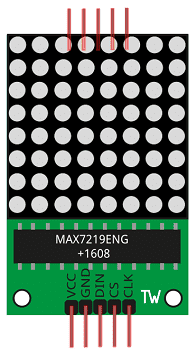
The MAX7219 is a serial input/output common-cathode display driver that can be used to drive a 7-segment LED display, or an 8×8 LED matrix. It is a compact and versatile integrated circuit that allows you to control multiple digits with a single digital output pin. The MAX7219 can interface with a microcontroller, such as an Arduino, via a 3-wire serial interface, which consists of Data, Clock, and Load pins. The MAX7219 also has built-in features such as a BCD decoder, a multiplex scan circuitry, and a digit driver. It requires an external power supply of 5V and can drive up to 8 digits, with a maximum current of 150mA per segment. The MAX7219 library can be used to control the MAX7219 display with the Arduino UNO, it’s easy to use and have a lot of functionality.
Test plate

A test plate for Arduino is a type of test plate that can be used in conjunction with an Arduino microcontroller to automate experiments or tests. The test plate typically contains multiple wells or compartments that can hold samples or test solutions, and is designed to interface with the Arduino’s digital inputs and outputs.
Connecting wires

Wires in a robotic system are used to connect and transmit electrical signals between different components of the robot. These components can include sensors, actuators, motors, and the microcontroller, such as an Arduino. The wires in a robotic system are typically made of copper and are insulated to prevent electrical interference and short circuits.
The type of wires used in a robotic system depends on the specific application and requirements of the robot. For example, a robot that requires high-current power transmission may use thicker, high-gauge wires, while a robot that requires a high degree of flexibility and movement may use thinner, more flexible wires.
Wires in a robotic system can be used to transmit power, control signals, and data between the different components of the robot. They can also be used to connect the robot to external devices, such as a computer or a power source. The proper use of wires is crucial for the robot to function properly, and a bad wiring can cause malfunction, safety hazards, and even damage to the equipment.
It is important to use the right type of wire for the right application, and it is also important to keep the wires organized and secure to prevent them from getting tangled, damaged, or disconnected.
Mounting
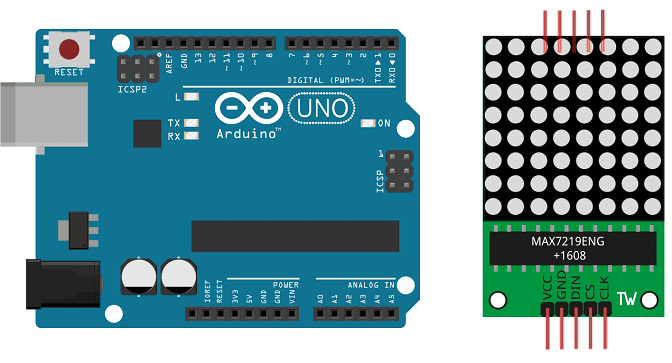
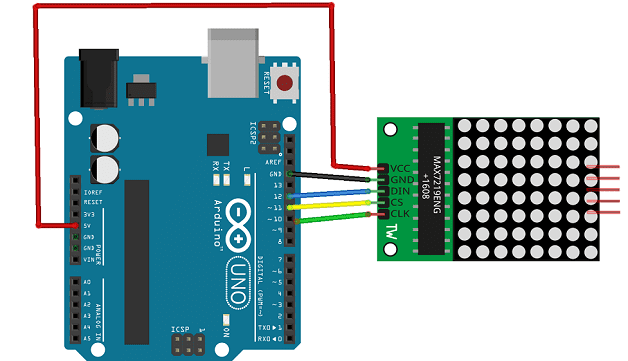
To perform the assembly, we connect:
-
the VCC pin of the display to the 3.3V pin of Arduino
-
the GND pin of the display to the GND pin of Arduino
-
pin DIN of the display to pin 12 of Arduino
-
the CS pin of the display to pin 11 of Arduino
-
the CLK pin of the display to pin 10 of Arduino
Arduino program
Here is the program which displays a character on the MAX7219 display.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 |
#include <LedControl.h> int DIN = 12; int CS = 11; int CLK = 10; byte e[8]= {0x7C,0x7C,0x60,0x7C,0x7C,0x60,0x7C,0x7C}; byte d[8]= {0x78,0x7C,0x66,0x66,0x66,0x66,0x7C,0x78}; byte u[8]= {0x66,0x66,0x66,0x66,0x66,0x66,0x7E,0x7E}; byte c[8]= {0x7E,0x7E,0x60,0x60,0x60,0x60,0x7E,0x7E}; byte eight[8]= {0x7E,0x7E,0x66,0x7E,0x7E,0x66,0x7E,0x7E}; byte s[8]= {0x7E,0x7C,0x60,0x7C,0x3E,0x06,0x3E,0x7E}; byte dot[8]= {0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x18,0x18}; byte o[8]= {0x7E,0x7E,0x66,0x66,0x66,0x66,0x7E,0x7E}; byte m[8]= {0xE7,0xFF,0xFF,0xDB,0xDB,0xDB,0xC3,0xC3}; LedControl lc=LedControl(DIN,CLK,CS,0); void setup(){ lc.shutdown(0,false); //The MAX72XX is in power-saving mode on startup lc.setIntensity(0,15); // Set the brightness to maximum value lc.clearDisplay(0); // and clear the display } void loop(){ byte smile[8]= {0x3C,0x42,0xA5,0x81,0xA5,0x99,0x42,0x3C}; byte neutral[8]= {0x3C,0x42,0xA5,0x81,0xBD,0x81,0x42,0x3C}; byte frown[8]= {0x3C,0x42,0xA5,0x81,0x99,0xA5,0x42,0x3C}; printByte(smile); delay(1000); printByte(neutral); delay(1000); printByte(frown); delay(1000); printEduc8s(); lc.clearDisplay(0); delay(1000); } void printEduc8s() { printByte(e); // display the letter 'e' delay(1000); printByte(d); // display the letter 'd' delay(1000); printByte(u); // afficher the letter 'u' delay(1000); printByte(c);// afficher the letter 'c' delay(1000); printByte(eight); delay(1000); printByte(s); delay(1000); printByte(dot); delay(1000); printByte(c); delay(1000); printByte(o); delay(1000); printByte(m); delay(1000); } void printByte(byte character []) { int i = 0; for(i=0;i<8;i++) { lc.setRow(0,i,character[i]); } } |