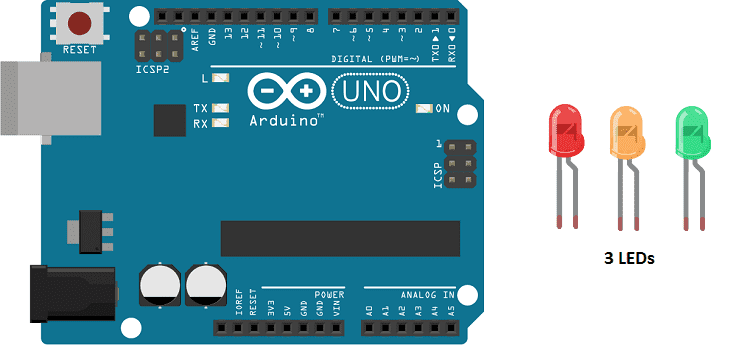

Presentation of traffic light
A traffic light is a signaling device at road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations to indicate when it is safe to drive, walk, or cycle. They are typically composed of three lights: red, yellow (or amber), and green. The red light indicates that vehicles or pedestrians should stop, the yellow light warns that the red signal is about to appear, and the green light indicates that it is safe to proceed. Traffic lights are used to control the flow of traffic and reduce collisions between vehicles, pedestrians, and bicycles. Some traffic lights also include additional features such as a walk signal for pedestrians and a left-turn signal for vehicles.
A traffic light with an LCD display controlled by an Arduino is a system that utilizes an Arduino microcontroller to control the operation of a traffic light and an LCD display to show the current status of the traffic light.
A traffic light controlled by an Arduino is a system that utilizes an Arduino microcontroller to control the operation of a traffic light. The Arduino is connected to the traffic light‘s lights (red, yellow, green) through its digital output pins and uses its programming capabilities to control when each light is on or off.
The system can be implemented by connecting the lights of the traffic light to the digital output pins of the Arduino and using the Arduino‘s programming to control the timing of the lights. For example, the red light can be on for a certain amount of time, followed by the yellow light for a short period, and then the green light. The timing can be adjusted as needed depending on the traffic flow or other factors.
Additionally, the Arduino can be programmed to control the traffic light based on input from sensors, such as a motion sensor or a traffic sensor, which detect the presence of cars or pedestrians. This can be used to optimize the traffic flow and reduce congestion at the intersection.
It would be a DIY project, it’s not commonly used in real-world traffic management systems.
Purpose of this project:
In this project we will create a traffic light controlled by the Arduino map where the Red led lights up for 3 seconds, then turns off and the Green LED lights up for 3 seconds and turns off so that the orange LED lights up for 1 second. Then the program starts at the beginning and starts again.
Necessary components
Arduino UNO
The Arduino UNO is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P. It has 14 digital input/output pins, 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button. It is the most popular and widely used board among the Arduino boards.
The Arduino UNO can be programmed using the Arduino programming language, which is based on C++. It uses a simple and intuitive programming environment, making it easy for beginners to get started with microcontroller programming.
The Arduino UNO can be connected to various sensors and actuators to control different devices and perform different tasks. For example, it can be used to control motors, read data from sensors, display information on an LCD screen, and communicate with other devices via serial communication protocols such as I2C and SPI.
The Arduino UNO can also be powered by a USB cable or an external power supply, making it easy to use in a wide range of projects and applications. It’s compatible with a wide range of shields (expansion boards) that adds functionality to the board, such as Ethernet, WiFi, and Bluetooth, and it’s widely supported by a strong and active community, which provides a lot of tutorials, examples and libraries to help users to get the most of the board.
Red LED- Yellow LED – Green LED
An LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current is passed through it. LEDs are widely used in a variety of applications because they are energy-efficient, have a long lifespan, and are available in a wide range of colors.
LEDs can be found in many electronic devices such as televisions, smartphones, computers, and traffic lights. They are also used in automotive lighting, general illumination, and as indicator lights.
3 220 ohm resistors
Resistors are passive electronic components that are used to control the flow of electric current in a circuit. They are typically made of a conductive material, such as carbon or metal, that resists the flow of electricity. The resistance of a resistor is measured in ohms (Ω). Resistors can be used to divide voltage, limit current, and bias active devices. They are widely used in electronic circuits for a wide range of applications.
connecting wires

Connecting wires are used to connect various components in an electronic circuit. They allow for the transfer of electricity, data, or signals between different devices and components.
When connecting wires to an Arduino or other microcontroller, it is important to pay attention to the correct pinout. The pinout refers to the arrangement of pins on the microcontroller and the corresponding function of each pin. The Arduino pinout can be found in the documentation provided by the manufacturer, or in various resources available online.
test plate

A test plate, also known as a test jig, is a device used to test electronic circuits and components. It is a board or plate that has been designed to hold and connect various components and devices in a specific configuration, allowing for the easy testing and measurement of their performance.
A test plate can be used to test various types of electronic circuits and components, such as microcontrollers, sensors, and actuators. It typically includes connectors and sockets for connecting wires, power supply and measurement devices such as multimeters, oscilloscopes, and power supplies.
Mounting
To complete the assembly, the green LED resistor can be connected to the digital PIN 0 , the yellow LED resistor to the PIN 1 and the red LED resistor to the PIN 2 of the Arduino.
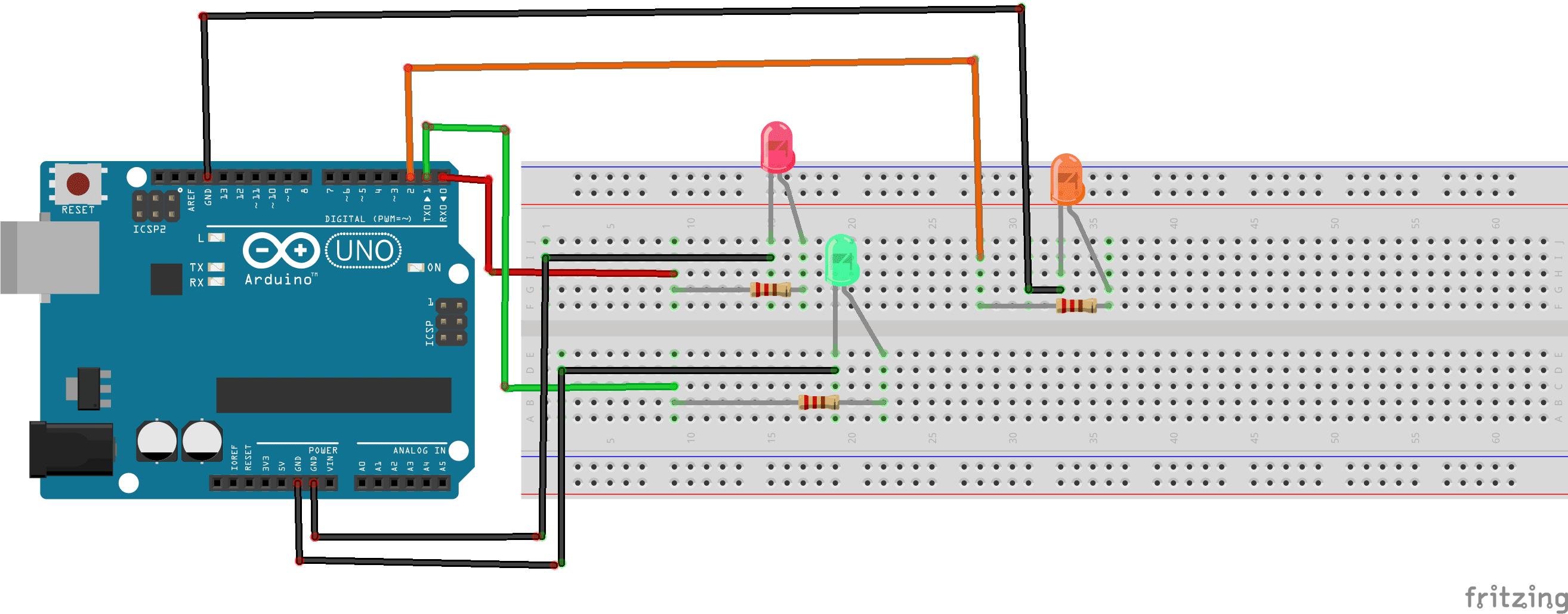
Programme
Voici le programme de feu de circulation :
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
void setup(){ pinMode(0,OUTPUT); //sets the number 0 digital pin of the Arduino in output mode pinMode(1,OUTPUT); //sets the number 1 digital pin of the Arduino in output mode pinMode(2,OUTPUT); //sets the number 2 digital pin of the Arduino in output mode } void loop(){ digitalWrite(0,HIGH); //red LED lights up digitalWrite(1,LOW); // green LED goes out digitalWrite(2,LOW); //orange LED goes out delay(3000); digitalWrite(0,LOW); //red LED goes out digitalWrite(1,HIGH); //green LED lights up digitalWrite(2,LOW); // orange LED goes out delay(1000); digitalWrite(0,LOW); //red LED goes out digitalWrite(1,LOW); // green LED goes out digitalWrite(2,HIGH); //orange LED lights up delay(3000); } |