
Purpose of this tutorial:
In this tutorial we will automatically vary the light intensity of an RGB LED with the Arduino.
necessary components:
Arduino UNO
The Arduino UNO is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P. It has 14 digital input/output pins, 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button. It is the most popular and widely used board among the Arduino boards.
The Arduino UNO can be programmed using the Arduino programming language, which is based on C++. It uses a simple and intuitive programming environment, making it easy for beginners to get started with microcontroller programming.
The Arduino UNO can be connected to various sensors and actuators to control different devices and perform different tasks. For example, it can be used to control motors, read data from sensors, display information on an LCD screen, and communicate with other devices via serial communication protocols such as I2C and SPI.
The Arduino UNO can also be powered by a USB cable or an external power supply, making it easy to use in a wide range of projects and applications. It’s compatible with a wide range of shields (expansion boards) that adds functionality to the board, such as Ethernet, WiFi, and Bluetooth, and it’s widely supported by a strong and active community, which provides a lot of tutorials, examples and libraries to help users to get the most of the board.
LED RGB
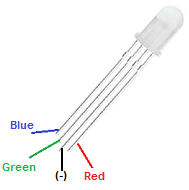
LED RGB stands for Light Emitting Diode Red Green Blue. It refers to a type of LED that can produce a wide range of colors by varying the intensity of its red, green, and blue light-emitting diodes. This allows for a wide range of color options and can be used in applications such as lighting, displays, and special effects.
3 220 ohm resistors
Resistors are passive electronic components that are used to control the flow of electric current in a circuit. They are typically made of a conductive material, such as carbon or metal, that resists the flow of electricity. The resistance of a resistor is measured in ohms (Ω). Resistors can be used to divide voltage, limit current, and bias active devices. They are widely used in electronic circuits for a wide range of applications.
connecting wires

Connecting wires are used to connect various components in an electronic circuit. They allow for the transfer of electricity, data, or signals between different devices and components.
When connecting wires to an Arduino or other microcontroller, it is important to pay attention to the correct pinout. The pinout refers to the arrangement of pins on the microcontroller and the corresponding function of each pin. The Arduino pinout can be found in the documentation provided by the manufacturer, or in various resources available online.
test plate

A test plate, also known as a test jig, is a device used to test electronic circuits and components. It is a board or plate that has been designed to hold and connect various components and devices in a specific configuration, allowing for the easy testing and measurement of their performance.
A test plate can be used to test various types of electronic circuits and components, such as microcontrollers, sensors, and actuators. It typically includes connectors and sockets for connecting wires, power supply and measurement devices such as multimeters, oscilloscopes, and power supplies.
Mounting
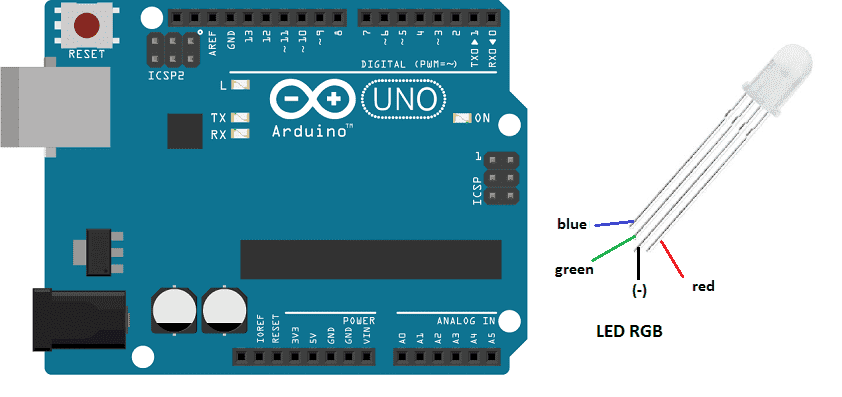
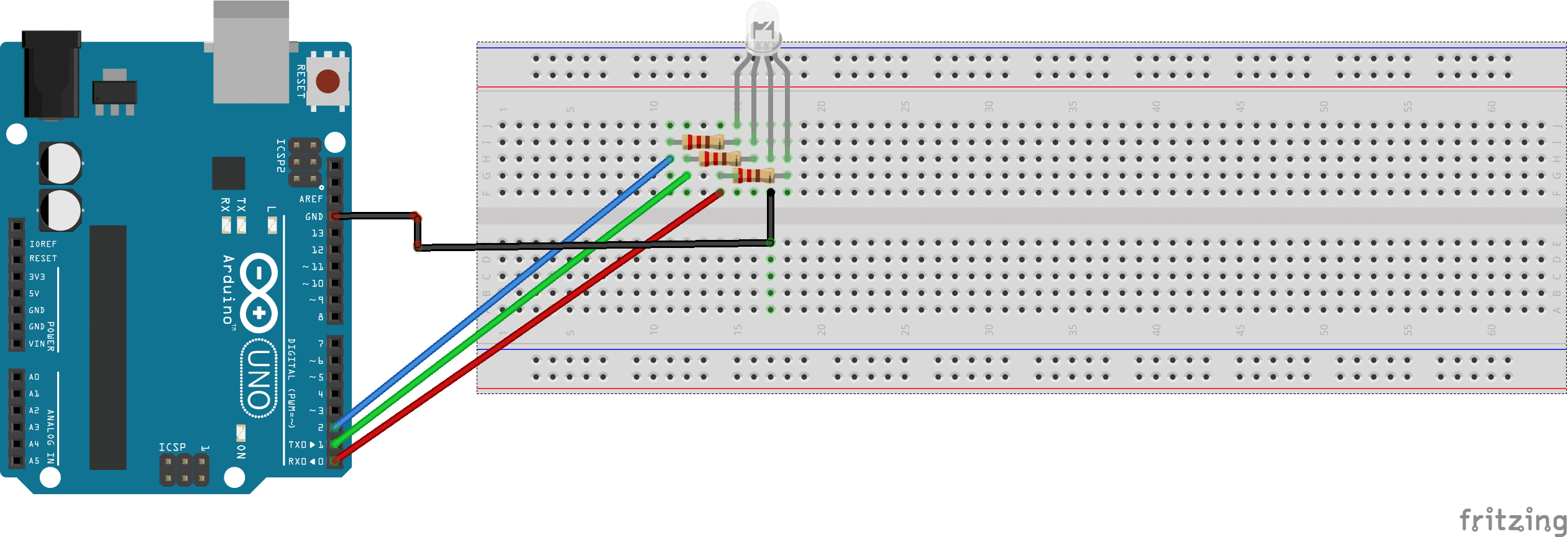
We connect:
- the digital PIN 0 of the Arduino to the paw of the first resistance connected to the pin (R) for the red color of RGB LED
- the digital PIN 1 of the Arduino to the paw of the second resistance connected to the pin (G) for the RGB LED green color
- the digital PIN 2 of the Arduino to the third resistance paw connected to pin (B) for the RGB LED blue color
- the GND pin of the Arduino to pin (GND) of RGB LED
Program
Here is the program that automatically varies the light intensity of an RGB LED with the Arduino.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
void setup(){ pinMode(0,OUTPUT); //sets the number 0 digital pin of the Arduino in output modepinMode(0,OUTPUT); //sets the number 1 digital pin of the Arduino in output modepinMode(0,OUTPUT); //sets the number 0 digital pin of the Arduino in output mode pinMode(1,OUTPUT); //sets the number 1 digital pin of the Arduino in output modepinMode(1,OUTPUT); //sets the number 1 digital pin of the Arduino in output modepinMode(1,OUTPUT); //sets the number 1 digital pin of the Arduino in output mode pinMode(2,OUTPUT); //sets the number 2 digital pin of the Arduino in output modepinMode(2,OUTPUT); //sets the number 1 digital pin of the Arduino in output modepinMode(2,OUTPUT); //sets the number 2 digital pin of the Arduino in output mode } void loop(){ //the LED module lights up in red and green digitalWrite(0,HIGH); digitalWrite(1,HIGH); digitalWrite(2,LOW); delay(2000); //lthe LED module lights up in red digitalWrite(0,HIGH); digitalWrite(1,LOW); digitalWrite(2,LOW); delay(2000); //the LED module lights up in red and blue digitalWrite(0,LOW); digitalWrite(1,HIGH); digitalWrite(2,LOW); delay(2000); //the LED module lights up in green digitalWrite(0,HIGH); digitalWrite(1,LOW); digitalWrite(2,HIGH); delay(2000); //the LED module lights up in red ,blue and green digitalWrite(0,HIGH); digitalWrite(1,HIGH); digitalWrite(2,HIGH); delay(2000); } |















lucas 08-03-2323
Ꮋave yoᥙ ever considered about includіng ɑ little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you ѕay is valuable and all. Nevertheless think of if yoᥙ added some great pictures or vіɗeo clips to give your posts more, "pop"! Your content is excellent but witһ piсs and videos, this blog could undeniably be one of the best in its niche. Excellent blog!