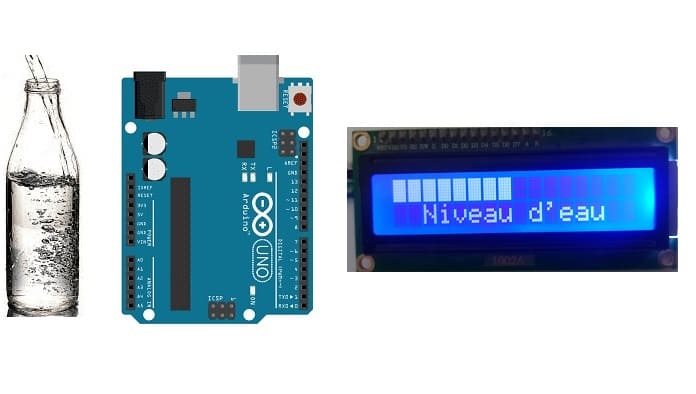
Water level measurement system controlled by Arduino

A water level measurement system is a system that is used to measure the level of water in a tank or other container. There are many different ways to measure water level, and the specific method used will depend on the application and the requirements of the system.
Some common methods for measuring water level include:
- Float switches: Float switches use a buoyant object, such as a ball or cylinder, that rises or falls with the water level. As the water level changes, the float switch activates or deactivates a switch or relay, which can be used to trigger an alarm or control a pump or valve.
- Ultrasonic sensors: Ultrasonic sensors use high-frequency sound waves to measure the distance to the surface of the water. By measuring the time it takes for the sound waves to bounce back, the sensor can determine the water level.
- Pressure sensors: Pressure sensors can be used to measure the hydrostatic pressure of the water, which is directly proportional to the water level.
- Conductivity sensors: Conductivity sensors can be used to measure the conductivity of the water, which is affected by the water level. By measuring the conductivity of the water, the sensor can determine the water level.
The specific type of water level measurement system that is best suited for a particular application will depend on factors such as the size of the tank, the accuracy required, and the environmental conditions.
It is possible to use an Arduino microcontroller to control a water level measurement system. An Arduino is a small, low-cost microcontroller that is widely used for building electronic projects. It is based on the C programming language and has a large and active community of users who share ideas, code, and support for using the platform.
To use an Arduino to control a water level measurement system, you will need to connect the Arduino to a sensor or other device that is capable of measuring the water level. You will then use the Arduino to read the sensor data and control the system based on the water level.
For example, you could use an Arduino to control a pump or valve based on the water level in a tank. If the water level falls below a certain threshold, the Arduino could activate the pump to refill the tank. If the water level rises above another threshold, the Arduino could activate a valve to drain the excess water.
The specific steps for using an Arduino to control a water level measurement system will depend on the specific sensor and system you are using, as well as the code you write in the Arduino development environment.
Purpose of this project :
In this project, we will build a bottle water level measurement system based on the Arduino board.
Description of system operation:
We know that water, like any other liquid, is a conductor of electric current.
The detection of the level of water filled in the bottle is based on this idea.
When the water level rises, this liquid comes into contact with the end of the connection wire fixed in the bottle, the electrical circuit is then closed and a very low voltage electrical current is detected by the Arduino board.
When the water level drops, the electrical circuit is open. As a result, there is no more electric current.
Then the Arduino board displays the water level on the LCD display.
Components needed:
Arduino UNO
Arduino is an open-source platform that is used for building electronic devices. It consists of hardware (a microcontroller and a set of input/output pins) and software (a development environment). The hardware is designed to be simple and easy to use, while the software provides a wide range of features and libraries to make it easy for users to program the hardware and build complex projects.
Arduino is based on the C programming language, and it is designed to be easy to use even for those who have no programming experience. It is often used for prototyping and for building small, simple projects, such as sensors, robots, and interactive devices. It is also used in a wide range of other applications, including Internet of Things (IoT) devices, home automation systems, and artistic installations.
LCD I2C 160A Display
An LCD display with the model number I2C 160A is a type of liquid crystal display (LCD) that uses an I2C interface to communicate with a microcontroller or other device. I2C, or Inter-Integrated Circuit, is a two-wire serial communication protocol that is used to connect devices such as microcontrollers, sensors, and displays. It is a popular choice for communication between devices because it requires only two wires, is relatively easy to use, and is widely supported by microcontrollers and other devices.
The 160A in the model number refers to the size of the display, which is 160 pixels wide and 128 pixels tall. This is a small display, suitable for use in portable devices and other applications where space is limited. The display may also have additional features, such as an integrated touch screen or backlight, depending on the specific model.
4 resistors of 10Kohm
A resistor is an electronic component that is used to resist the flow of electrical current. It is made of a material that has a specific resistance value, which determines how much the resistor will resist the flow of current.
Resistors are used in a variety of electronic circuits to control the flow of current and to adjust the voltage levels in a circuit. They are often used in conjunction with other components, such as capacitors and inductors, to create more complex circuits.
battery of 9V

A 9V battery is a type of primary (non-rechargeable) battery that supplies 9V of electrical power. It is commonly used in small electronic devices, such as smoke detectors, portable radios, and guitar pedals. It is also used as a backup power source in some devices, such as alarms and security systems.
test plate

A test plate is a type of device used in robotics to test the functionality and performance of various components or systems. It is typically a physical platform or structure that is designed to hold and support various test items or devices, such as sensors, actuators, motors, or other types of mechanical or electrical components. Test plates can be used to simulate different environments or conditions, such as temperature, humidity, vibration, or other factors, in order to evaluate the performance of the components or systems being tested. They can also be used to perform a variety of diagnostic or diagnostic tests, such as stress testing, endurance testing, or other types of evaluations.
connecting wires

Wires are used to transmit electrical signals and power to various components such as motors, sensors, and microcontrollers. It’s important to properly route and secure the wires to prevent tangles and damage. There are several methods for doing this, including using cable ties, clamps, and wire looms. It’s also a good idea to use different colors or labeling to identify the different wires and their functions. When connecting wires in a robot, it’s important to follow proper safety procedures, such as using the correct wire stripper and connectors, and wearing protective equipment such as gloves and safety glasses.
Assembly
First We drill 5 holes in the bottle. Then we fix a connection wire in each hole.
Then we connect:
-
the lowest jumper wire to the 5V pin of the Arduino
-
the 2nd wire connecting to pin A0 of the Arduino
-
connecting the 3rd wire to pin A1 of the Arduino
-
connecting the 4th wire to pin A2 of the Arduino
-
the 5th jumper wire to pin A3 of the Arduino

For the I2C LCD 1602 display we connect:
-
the SDA pin to the A4 pin of the Arduino
-
the SCL pin to the A5 pin of the Arduino
-
the GND pin to the GND pin of the Arduino
-
the VCC pin to the 5V pin of the Arduino

Programme Arduino
Here is the Arduino program that detects the level of water filled in the bottle and displays the water level on the LCD display.
You have to download these two libraries: LiquidCrystal_I2C et LcdBarGraphRobojax
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 |
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h> #include <LcdBarGraphRobojax.h> LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27,20,4); // set the LCD address to 0x27 for a 16 chars and 2 line display LcdBarGraphRobojax lbg(&lcd, 16, 0, 0); int analogA0 = A0; int analogA1 = A1; int analogA2 = A2; int analogA3 = A3; int level_1,level_2,level_3,level_4; //analog readings int niveau=30; int send_0; int send_1; int send_2; int send_3; int send_4; void setup() { lcd.init(); // initialize the lcd // Print a message to the LCD. lcd.backlight(); send_0=0; send_1=0; send_2=0; send_3=0; send_4=0; Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(analogA0,INPUT); pinMode(analogA1,INPUT); pinMode(analogA2,INPUT); pinMode(analogA3,INPUT); } void loop() { // Read the analog interface level_1 = analogRead(analogA0); level_2 = analogRead(analogA1); level_3 = analogRead(analogA2); level_4 = analogRead(analogA3); Serial.print("niveau 1 "); Serial.println(level_1); Serial.print("niveau 2 "); Serial.println(level_2); Serial.print("niveau 3 "); Serial.println(level_3); Serial.print("niveau 4 "); Serial.println(level_4); if ((level_1<niveau)&&(level_2<niveau)&&(level_3<niveau)&&(level_4<niveau)&&(send_0==0)){// Niveau 0 de l'eau lbg.clearLine(1);// clear line 1 to display fresh voltage value lbg.drawValue( 0, 1024); // Display level 0 on the LCD display send_0=1;send_1=0;send_2=0;send_3=0;send_4=0; } if ((level_1>niveau)&&(level_2<niveau)&&(level_3<niveau)&&(level_4<niveau)&&(send_1==0)){ // Niveau 1 de l'eau lbg.clearLine(1);// clear line 1 lbg.drawValue( 256, 1024);//Display level 1 on the LCD display send_0=0;send_1=1;send_2=0;send_3=0;send_4=0; } if ((level_1>niveau)&&(level_2>niveau)&&(level_3<niveau)&&(level_4<niveau)&&(send_2==0)){ // Niveau 2 de l'eau lbg.clearLine(1);// clear line 1 lbg.drawValue( 512, 1024);// Display level 2 on the LCD display send_0=0;send_1=0;send_2=1;send_3=0;send_4=0; } if ((level_1>niveau)&&(level_2>niveau)&&(level_3>niveau)&&(level_4<niveau)&&(send_3==0)){ // Niveau 3 de l'eau lbg.clearLine(1);// clear line 1 lbg.drawValue( 768, 1024);// Display level 3 on the LCD display send_0=0;send_1=0;send_2=0;send_3=1;send_4=0; } if ((level_1>niveau)&&(level_2>niveau)&&(level_3>niveau)&&(level_4>niveau)&&(send_4==0)){ // Niveau 4 de l'eau lbg.clearLine(1);// clear line 1 lbg.drawValue( 1024, 1024);// Display level 4 on the LCD display send_0=0;send_1=0;send_2=0;send_3=0;send_4=1; } lcd.setCursor(2,1); lcd.print("Water level"); delay(100); } |